Contents [hide]
One to Many Mapping
One To Many mapping to represent one to many relationships between tables. A one to many relationships occurs between tables when one record from a table can correspond to many records from another table.
For example, In a department, many employees work. So one record in the Department table will correspond to many records in the Employee table.

Tools and Technologies Used:
1. Java 8
2. MySQL 8
3. Eclipse IDE
4. mysql-connector-java-8.0.23.jar
5. Hibernate 5.5.7.Final
6. Maven 3.6.1
Maven Project for One to Many Mapping
We need to follow below steps:
Step 1: Click on File --> New --> Maven Project.
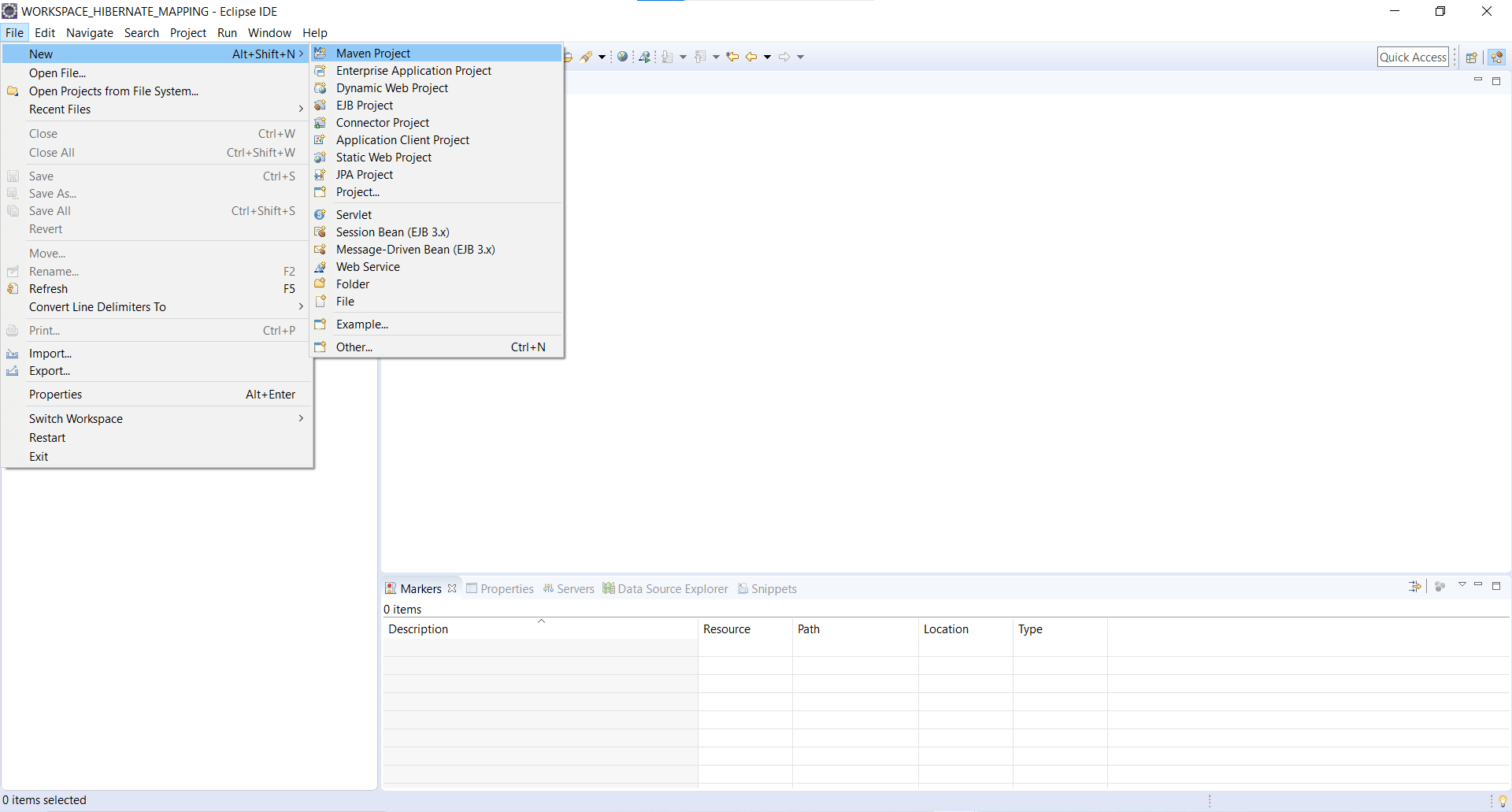
Step 2: Check Checkbox Create a simple project (skip archetype selection). Click on Next button.
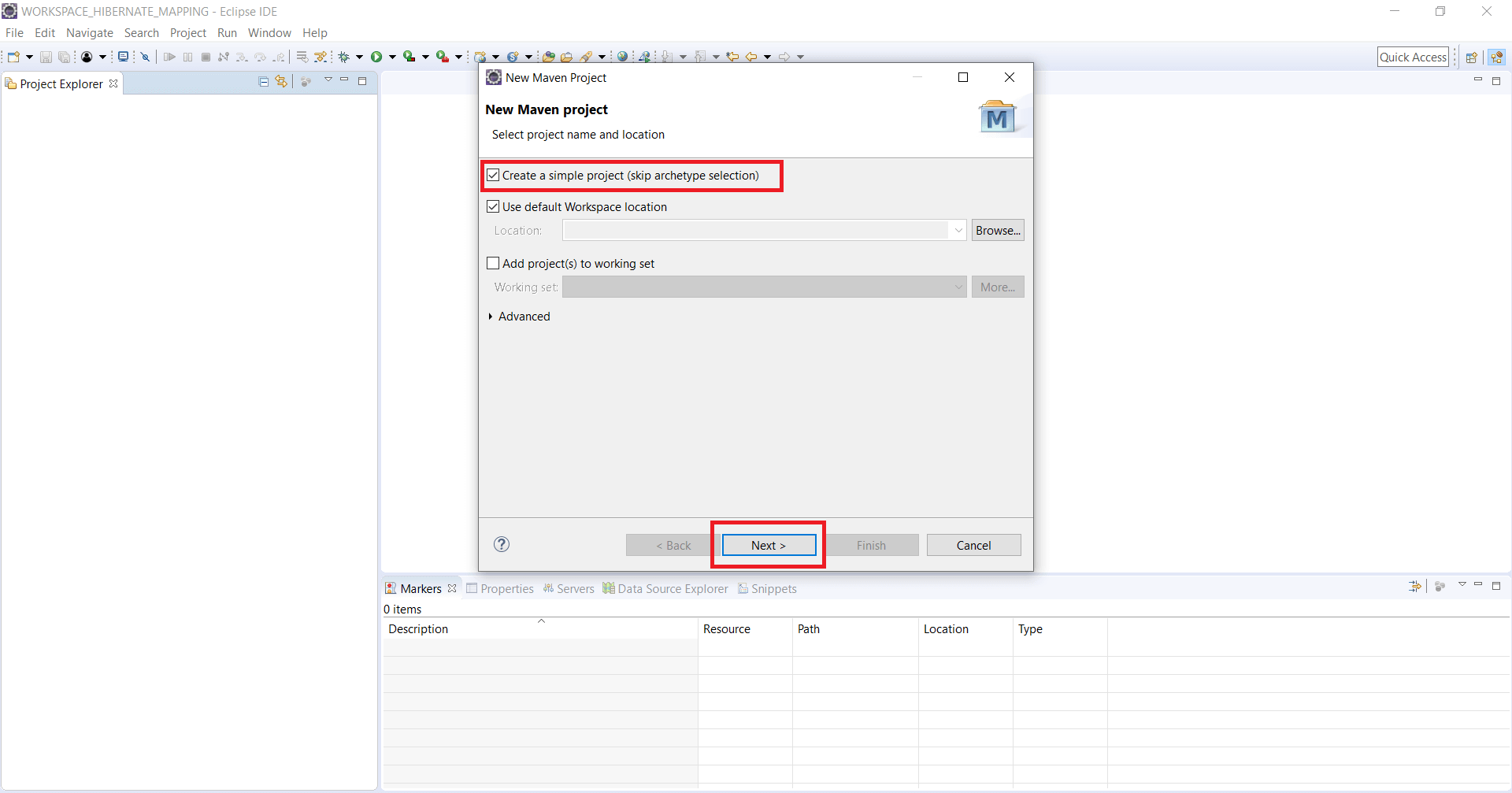
Step 3: Enter Group Id, Artifact Id, Version, Packaging, Name, Description details and click on Finish button.
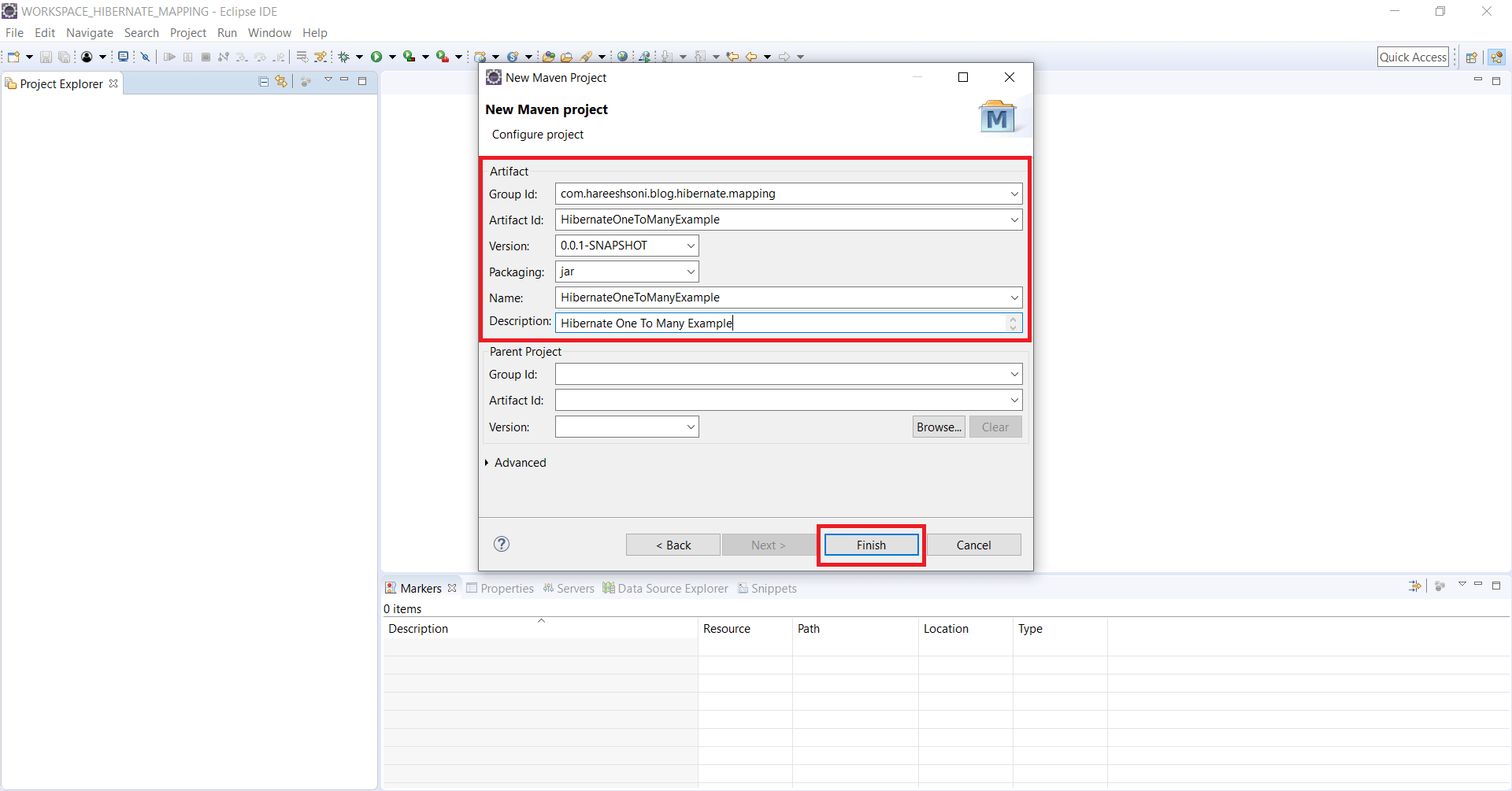
Update pom.xml file.
Open pom.xml file and paste below pom.xml file code.
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.hareeshsoni.blog.hibernate.mapping</groupId> <artifactId>HibernateOneToManyExample</artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> <name>HibernateOneToManyExample</name> <description>Hibernate One To Many Example</description> <dependencies> <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.hibernate/hibernate-core --> <dependency> <groupId>org.hibernate</groupId> <artifactId>hibernate-core</artifactId> <version>5.5.7.Final</version> </dependency> <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/mysql/mysql-connector-java --> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <version>8.0.23</version> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <finalName></finalName> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId> <artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId> <version>3.6.1</version> <configuration> <source>1.8</source> <target>1.8</target> </configuration> </plugin> </plugins> </build> </project>
Update Maven Project
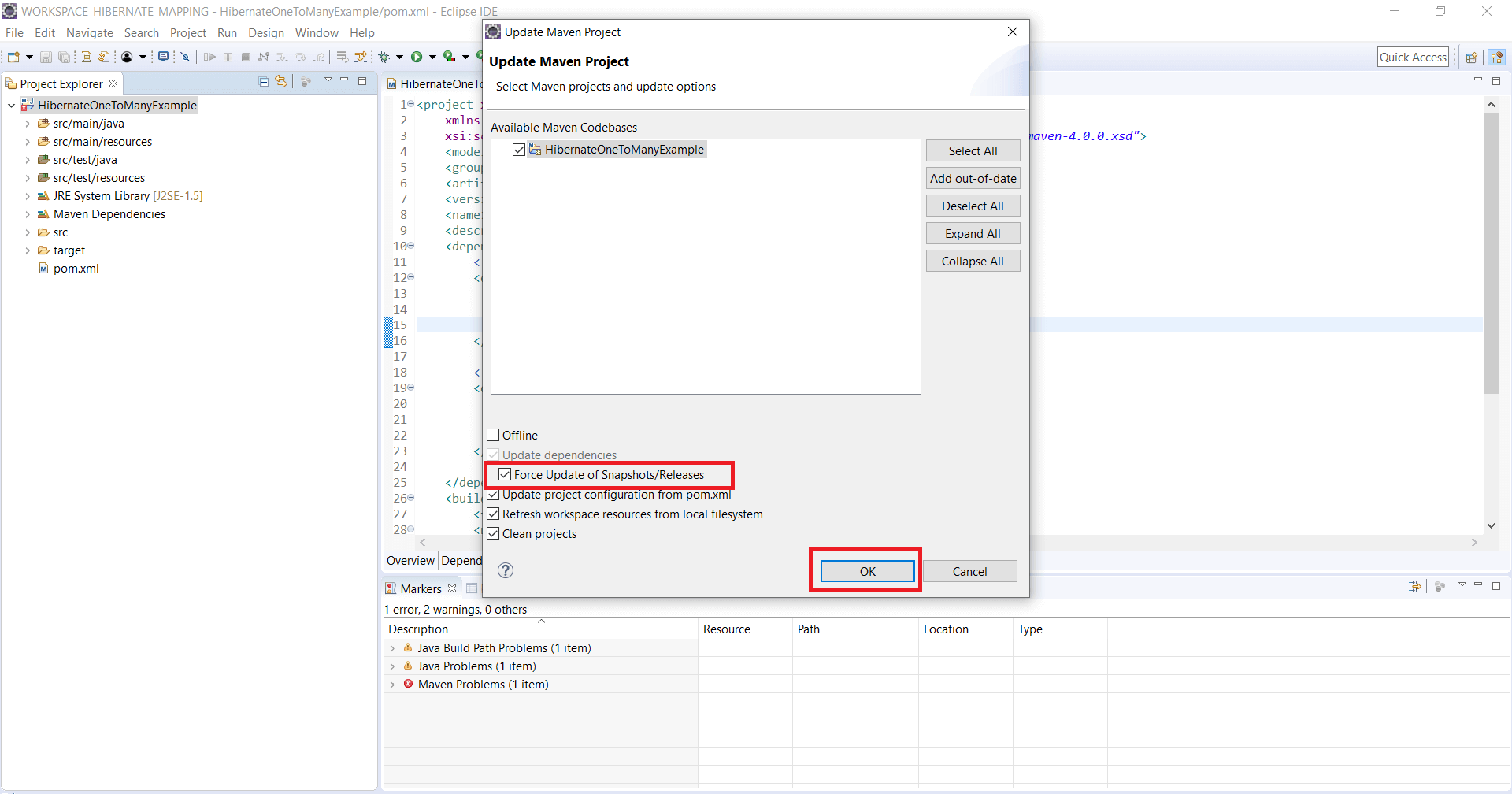
Step 1: Right-click on project HibernateOneToManyExample --> Maven --> Update Project…
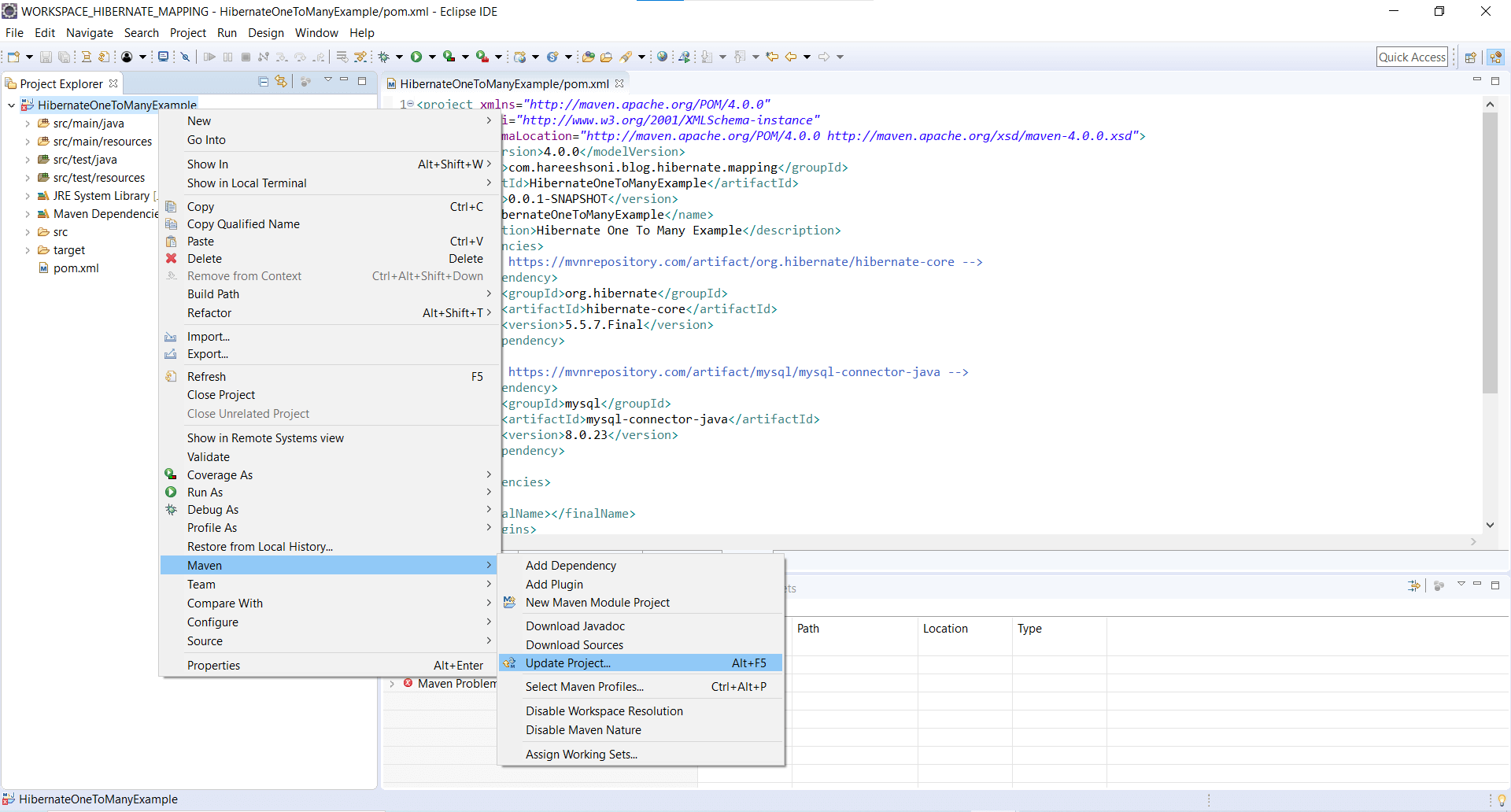
Step 2: Check Checkbox Force Update of Snapshots/Releases. Click on OK Button.

We have used the below JPA Annotations:
@Entity: @Entity annotation specifies that the class is an entity.
@Table: @Table annotation specifies the primary table for the annotated entity.
@Id: @Id annotation marks the particular field as the primary key of the Entity.
@GeneratedValue: This annotation is used to specify how the primary key should be generated.
@Column: This annotation maps the corresponding fields to their respective columns in the database table.
@JoinColumn: This annotation defines the foreign key. It is the column that associates the two tables.
@OneToMany: This annotation is used to create one to many relationship between Department and Employee entities.
@ManyToOne: This annotation is used to create many to one relationship between Employee and Department entities.
package com.hareeshsoni.blog.hibernate.mapping.model;
import java.util.Set;
import javax.persistence.CascadeType;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.OneToMany;
import javax.persistence.Table;
@Entity
@Table(name = "department")
public class Department {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
@Column(name = "department_id")
private int departmentId;
@Column(name = "department_name")
private String departmentName;
@OneToMany(mappedBy = "department", cascade = CascadeType.ALL)
private Set employee;
public Department() {
}
public Department(String departmentName) {
this.departmentName = departmentName;
}
public int getDepartmentId() {
return departmentId;
}
public void setDepartmentId(int departmentId) {
this.departmentId = departmentId;
}
public String getDepartmentName() {
return departmentName;
}
public void setDepartmentName(String departmentName) {
this.departmentName = departmentName;
}
public Set getEmployee() {
return employee;
}
public void setEmployee(Set employee) {
this.employee = employee;
}
}
package com.hareeshsoni.blog.hibernate.mapping.model;
import javax.persistence.CascadeType;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.JoinColumn;
import javax.persistence.ManyToOne;
import javax.persistence.Table;
@Entity
@Table(name = "employee")
public class Employee {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
@Column(name = "employee_id")
private int employeeId;
@Column(name = "employee_name")
private String employeeName;
@ManyToOne(cascade = CascadeType.ALL)
@JoinColumn(name = "department_id")
private Department department;
public Employee() {
}
public Employee(String employeeName) {
this.employeeName = employeeName;
}
public int getEmployeeId() {
return employeeId;
}
public void setEmployeeId(int employeeId) {
this.employeeId = employeeId;
}
public String getEmployeeName() {
return employeeName;
}
public void setEmployeeName(String employeeName) {
this.employeeName = employeeName;
}
public Department getDepartment() {
return department;
}
public void setDepartment(Department department) {
this.department = department;
}
}
package com.hareeshsoni.blog.hibernate.mapping.util;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
public class HibernateUtil {
private static SessionFactory sessionFactory;
private static SessionFactory buildSessionFactory() {
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
configuration.configure("hibernate.cfg.xml");
System.out.println("Hibernate configuration file loaded");
SessionFactory sessionFactory = configuration.buildSessionFactory();
return sessionFactory;
}
public static SessionFactory getSessionFactory() {
if(sessionFactory == null)
sessionFactory = buildSessionFactory();
return sessionFactory;
}
}
In hibernate.cfg.xml file provide correct username and password.
Create database name "one_to_many_mapping" inside mysql database.
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='utf-8'?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD 3.0//EN" "http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd"> <hibernate-configuration> <session-factory> <!-- Database connection settings --> <property name="hibernate.connection.driver_class">com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver</property> <property name="hibernate.connection.url">jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/one_to_many_mapping</property> <property name="hibernate.connection.username">root</property> <property name="hibernate.connection.password">########</property> <property name="hibernate.dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5Dialect</property> <property name="show_sql">true</property> <property name="hbm2ddl.auto">update</property> <mapping class="com.hareeshsoni.blog.hibernate.mapping.model.Employee" /> <mapping class="com.hareeshsoni.blog.hibernate.mapping.model.Department" /> </session-factory> </hibernate-configuration>
package com.hareeshsoni.blog.hibernate.mapping;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import com.hareeshsoni.blog.hibernate.mapping.model.Department;
import com.hareeshsoni.blog.hibernate.mapping.model.Employee;
import com.hareeshsoni.blog.hibernate.mapping.util.HibernateUtil;
public class MainApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SessionFactory sessionFactory = HibernateUtil.getSessionFactory();
Session session = sessionFactory.openSession();
session.beginTransaction();
Department department = new Department("Human Resource");
Employee employee1 = new Employee("Mohan");
employee1.setDepartment(department);
session.save(employee1);
Employee employee2 = new Employee("Rohan");
employee2.setDepartment(department);
session.save(employee2);
session.getTransaction().commit();
session.close();
sessionFactory.close();
}
}
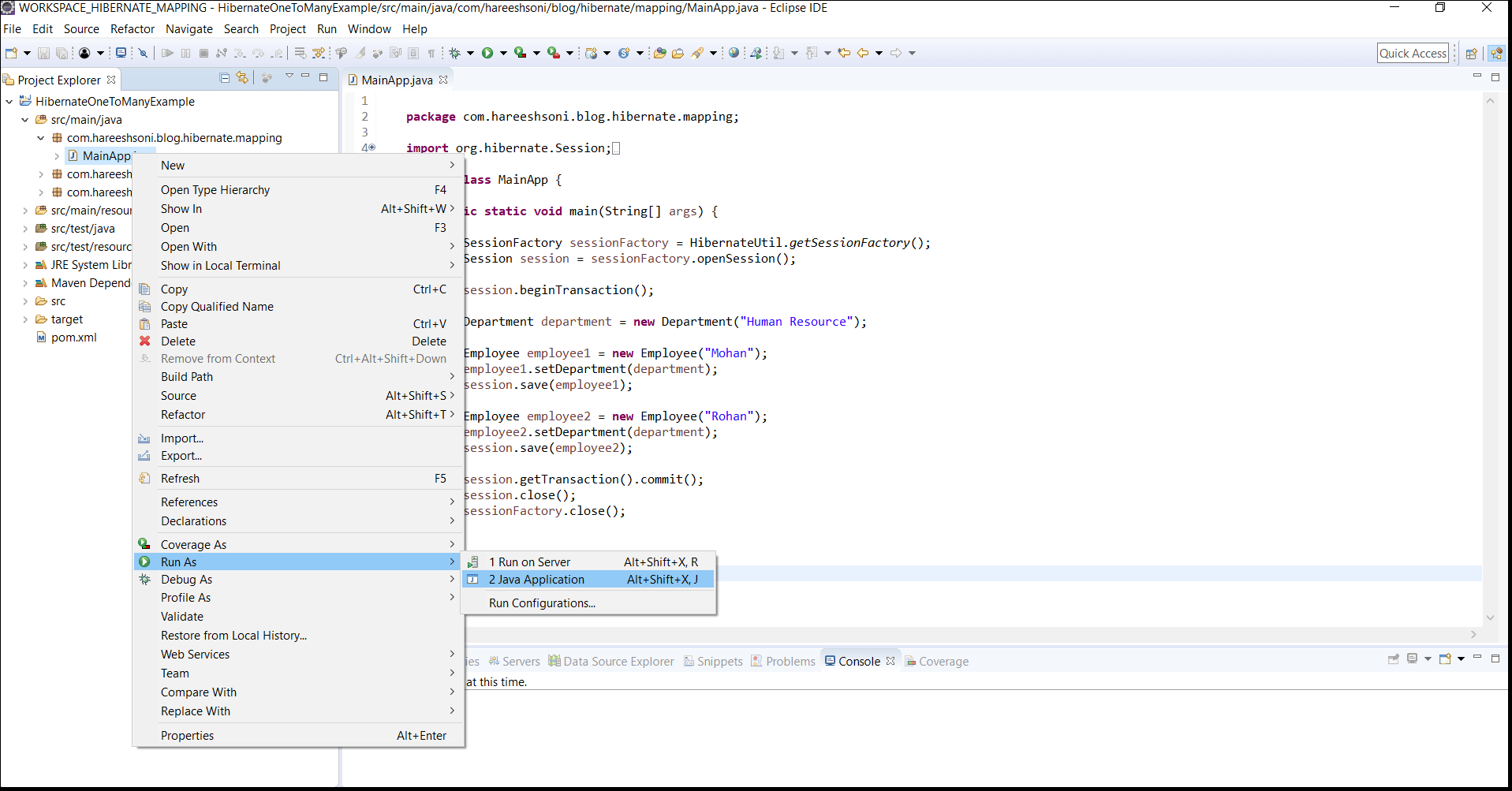
Now run MainApp.java
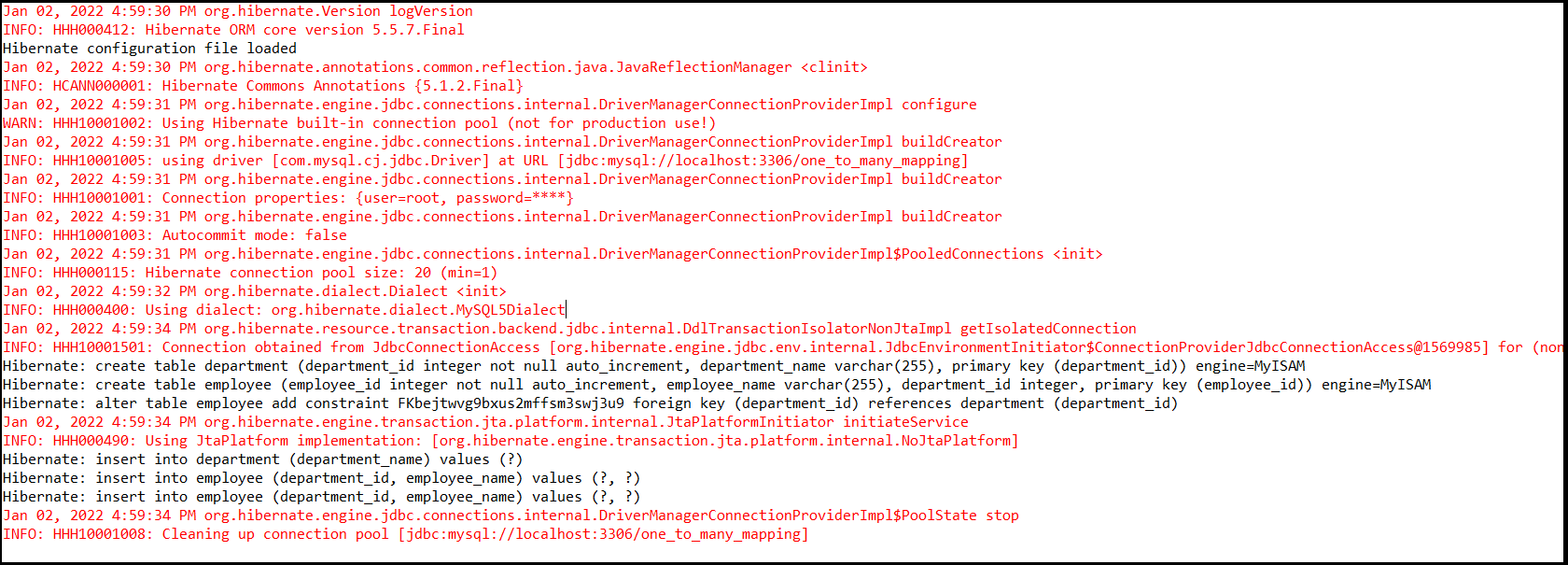
Output
Database tables:
Department Table

Employee Table
